Bidirectional Bandwidth Coordination under Half-Duplex Bottlenecks for Video Streaming
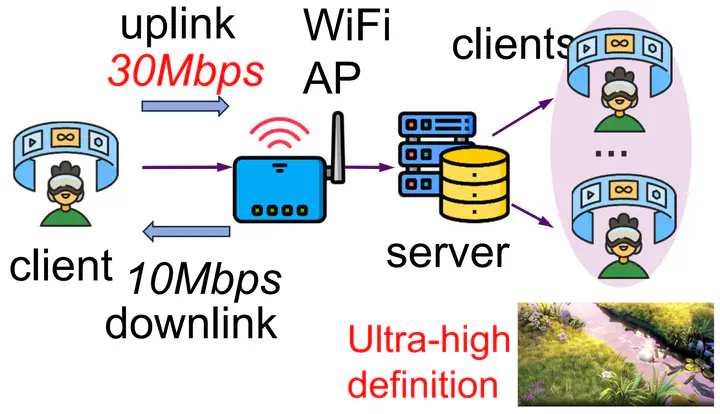 Illustration of Plum bandwidth coordination
Illustration of Plum bandwidth coordinationAbstract
Many video streaming applications will simultaneously transfer data in both directions, from the user to the Internet (uplink) and from the Internet to users (downlink). However, for wireless local area networks (WLANs), the dominant scenarios, the uplink and downlink flows share the same halfduplex physical channel and compete for bandwidth resources. Their bandwidths would be fairly apportioned under the existing link layer access method, but a fair share might be suboptimal for applications. For better application performance, we propose Plum, to coordinate the bitrate of uplink and downlink flows, and allocate the bandwidth in both directions to cater to the application’s demands. To make the deployment of Plum practical, we aim at not modifying the link layer but optimizing the transport layers and above. We evaluate our mechanisms with simulations based on real-world traces and testbed experiments, and results show that Plum could improve the video bitrate of streaming applications by up to 48-59%.